Page 79 - 机械工程材料2024年第十一期
P. 79
邸英南,等:不同冶炼工艺生产H13钢中非金属夹杂物特征及其对力学性能的影响
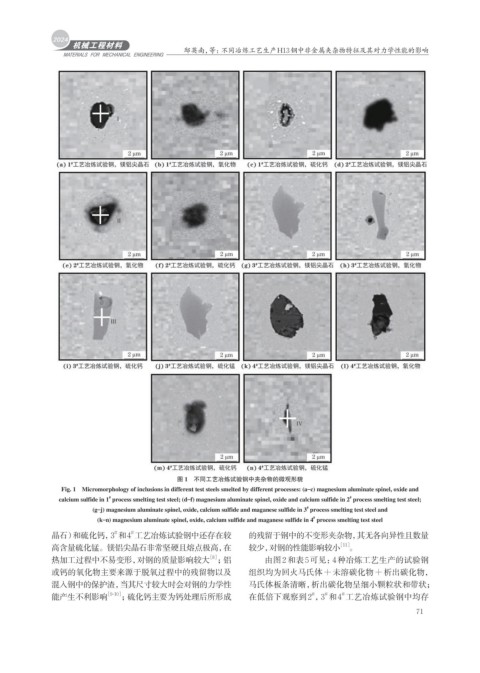
图 1 不同工艺冶炼试验钢中夹杂物的微观形貌
Fig. 1 Micromorphology of inclusions in different test steels smelted by different processes: (a–c) magnesium aluminate spinel, oxide and
#
#
calcium sulfide in 1 process smelting test steel; (d–f) magnesium aluminate spinel, oxide and calcium sulfide in 2 process smelting test steel;
#
(g–j) magnesium aluminate spinel, oxide, calcium sulfide and maganese sulfide in 3 process smelting test steel and
#
(k–n) magnesium aluminate spinel, oxide, calcium sulfide and maganese sulfide in 4 process smelting test steel
#
晶石)和硫化钙,3 和4 工艺冶炼试验钢中还存在较 的残留于钢中的不变形夹杂物,其无各向异性且数量
#
高含量硫化锰。镁铝尖晶石非常坚硬且熔点极高,在 较少,对钢的性能影响较小 [11] 。
[8]
热加工过程中不易变形,对钢的质量影响较大 ;铝 由图2和表5可见:4种冶炼工艺生产的试验钢
或钙的氧化物主要来源于脱氧过程中的残留物以及 组织均为回火马氏体+未溶碳化物+析出碳化物,
混入钢中的保护渣,当其尺寸较大时会对钢的力学性 马氏体板条清晰,析出碳化物呈细小颗粒状和带状;
#
能产生不利影响 [9-10] ;硫化钙主要为钙处理后所形成 在低倍下观察到2 ,3 和4 工艺冶炼试验钢中均存
#
#
71