Page 81 - 机械工程材料2024年第十一期
P. 81
邸英南,等:不同冶炼工艺生产H13钢中非金属夹杂物特征及其对力学性能的影响
2 200 抗拉强度 屈服强度 80 在这些细小的夹杂物和基体处形成显微孔洞,并在
断面收缩率 断后伸长率 70 [16]
2 000 滑移的作用下长大并相互连接形成韧窝 ,这些韧
60
1 800 50 窝分布均匀且尺寸较小,因此该工艺冶炼试验钢表
强度/MPa 1 600 40 30 断面收缩率、断后伸长率/% 现出更好的拉伸性能。在3 工艺冶炼试验钢中,大
#
尺寸且坚硬的镁铝尖晶石夹杂物的存在以及碳化物
1 400
20 颗粒的破碎致使其塑性较低。
1 200
10
1 000 0 3 结 论
1 工艺冶 2 工艺冶 3 工艺冶 4 工艺冶
#
#
#
#
炼试验钢 炼试验钢 炼试验钢 炼试验钢
(1)真空感应+真空自耗(VIM+VAR)工艺生
图 4 不同工艺冶炼试验钢的室温拉伸性能
Fig. 4 Tensile properties at room temperature of different test steels 产的H13钢中硫含量较低,非金属夹杂物含量较少
smelted by different processes 且尺寸较小,钢材的洁净度较高。
#
4 工艺冶炼试验钢(位置4)中发现硫化锰类型的夹 (2)4种冶炼工艺生产的H13钢回火后的组织均
杂物 [6-7] 。第二相质点对韧窝的形核起到重要的作用。 为回火马氏体+未溶碳化物+析出碳化物。VIM+
1 工艺冶炼试验钢中的夹杂物数量少、尺寸小,这使 VAR工艺生产的H13 钢与电弧炉+炉外精炼+
#
得其在拉伸过程中需要经历更大的塑性变形,才能 真空脱气+保护气氛电渣重熔 (EAF+LF+VD+
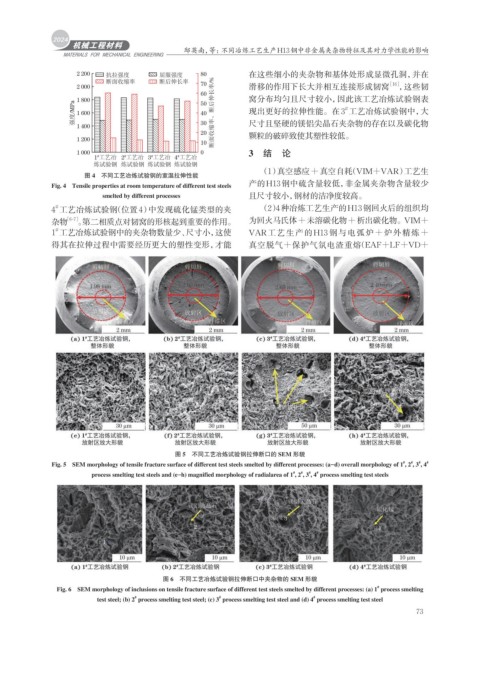
图 5 不同工艺冶炼试验钢拉伸断口的 SEM 形貌
#
#
#
Fig. 5 SEM morphology of tensile fracture surface of different test steels smelted by different processes: (a–d) overall morphology of 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 #
#
#
#
process smelting test steels and (e–h) magnified morphology of radialarea of 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 process smelting test steels
#
图 6 不同工艺冶炼试验钢拉伸断口中夹杂物的 SEM 形貌
Fig. 6 SEM morphology of inclusions on tensile fracture surface of different test steels smelted by different processes: (a) 1 process smelting
#
#
test steel; (b) 2 process smelting test steel; (c) 3 process smelting test steel and (d) 4 process smelting test steel
#
#
73